Discover the POWER of our Data Annotation Services !
Fill out the form below to schedule a personalized demo and see how we can transform your business.

Fill out the form below to schedule a personalized demo and see how we can transform your business.
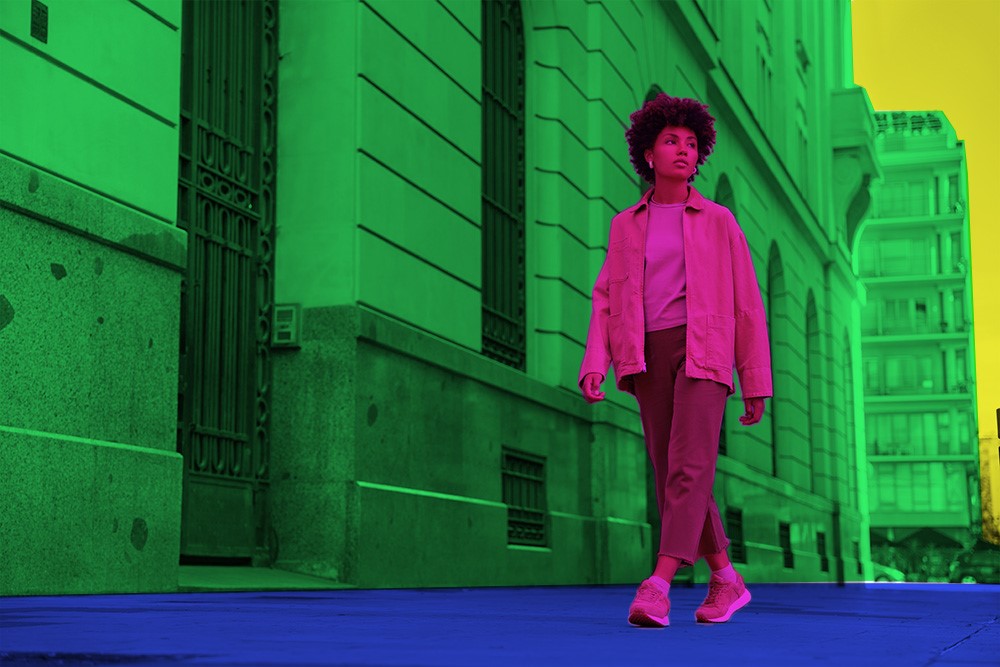


Applications of Semantic Segmentation:
Medical: Map entire DICOM slices of organs for detailed medical imaging.
Geospatial: Monitor deforestation or urbanization areas on satellite imagery for environmental analysis.
Automotive: Identify every element in a road scene for advanced driver-assistance systems.
Industrial: Segment casting defects on metallic parts for quality control in manufacturing.
Agriculture: Distinguish crops from weeds to optimize herbicide usage for precision farming.
Retail: Create virtual dressing rooms that distinguish users from the background for an enhanced shopping experience.

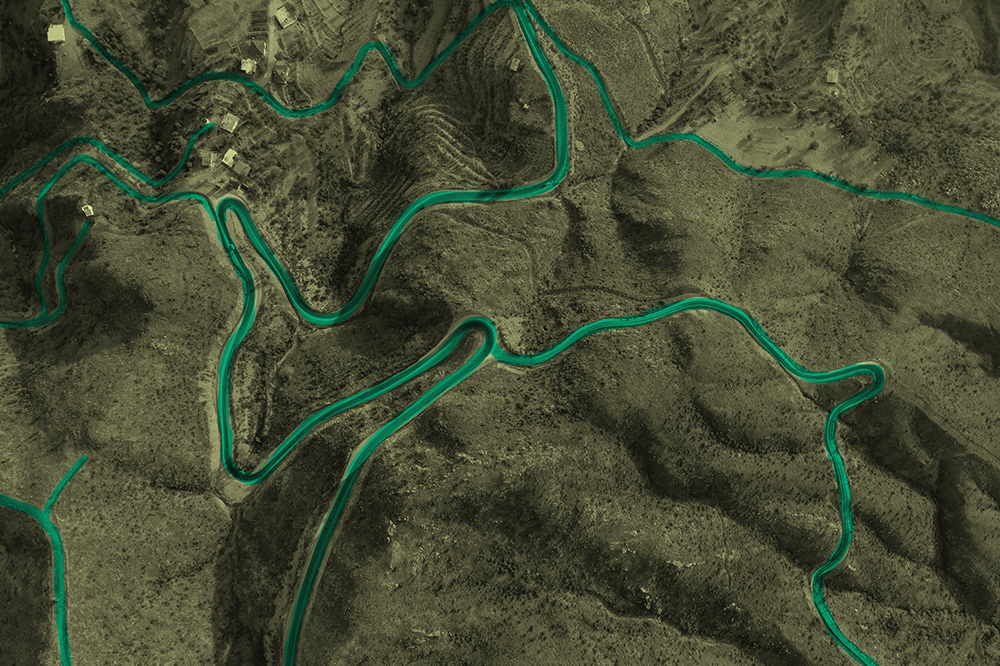

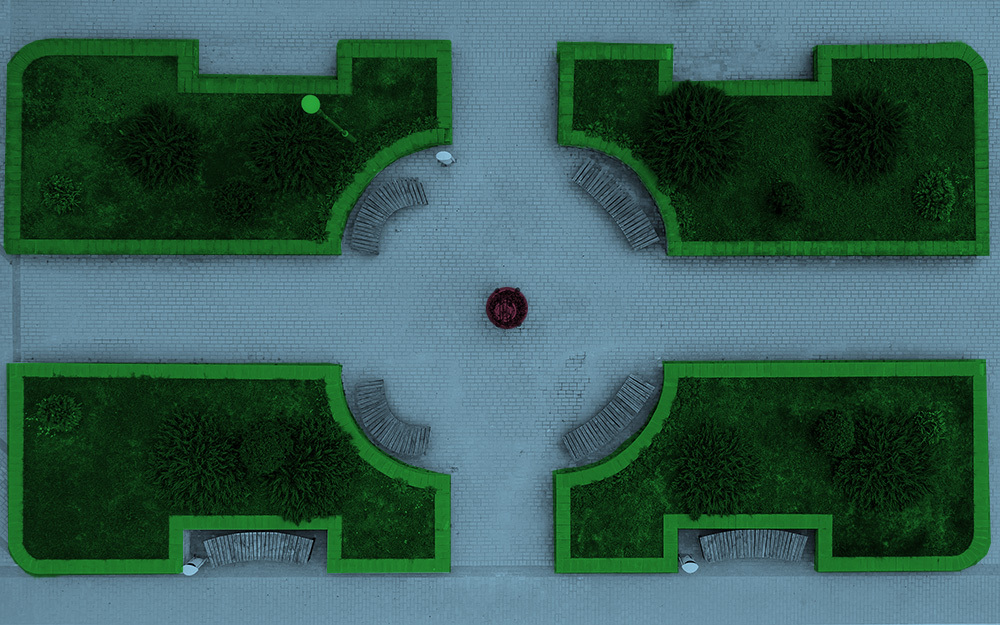
Advantages:
Ultra-Precise Labeling:
Advancements in Automation:
Disadvantages:
Time-Consuming Manual Segmentation:
Limitation in Identifying Instances and Overlaps:
Choosing the Right Tool for Manual Segmentation:
Precision with Polygons:
Consider Instance Segmentation for Quantity Information:
Enhanced Segmentation for Adjacent Objects:










Get a dedicated project manager to handle everything from guidelines to quality control, ensuring a seamless experience from start to finish.
Experience the assurance of multi-tiered QC processes, including peer review and expert checks, guaranteeing a minimum accuracy of 98%.
Access a diverse team of industry experts, assembled within 72 hours, tailored to fit your project's specific needs and scale.
Rely on our rigorously trained workforce for unbiased data, perfectly aligned with international privacy and AI standards.
Benefit from our dynamic workforce, capable of rapidly scaling up to meet tight deadlines and ensure swift project delivery.
Make a difference with every project; our entire workforce comes from refugee and disadvantaged backgrounds, contributing to social goals.
Fill out the form below to schedule a personalized demo and see how we can transform your business.
Fill out the form below to schedule a personalized demo and see how we can transform your business.
Semantic Segmentation classifies each pixel in an image, providing detailed labels for objects and boundaries.
It uniquely assigns semantic labels to pixels, offering a comprehensive understanding of image content.
Applied in autonomous driving, medical image analysis, satellite interpretation, and augmented reality for precise object detection.
Challenges include handling complex scenes, ensuring accurate pixel-level labeling, and managing computational demands.
Popular algorithms like CNNs, U-Net, and DeepLab use deep learning to achieve accurate pixel-level predictions.
Yes, with optimized algorithms and hardware, Semantic Segmentation is effective for real-time tasks like video analysis and robotics in dynamic environments.