Polygon Annotation: The Precise Way to Label Objects in Images for Machine Learning
In the ever-evolving world of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), particularly computer vision, accurately labeling data is the lifeblood of training effective models.
Just like a chef relies on fresh ingredients to craft a delicious meal, machine learning models depend on high-quality labeled data to perform tasks like object detection and image segmentation.
This is where polygon annotation steps in, offering a meticulous way to achieve this goal.
What is Polygon Annotation?

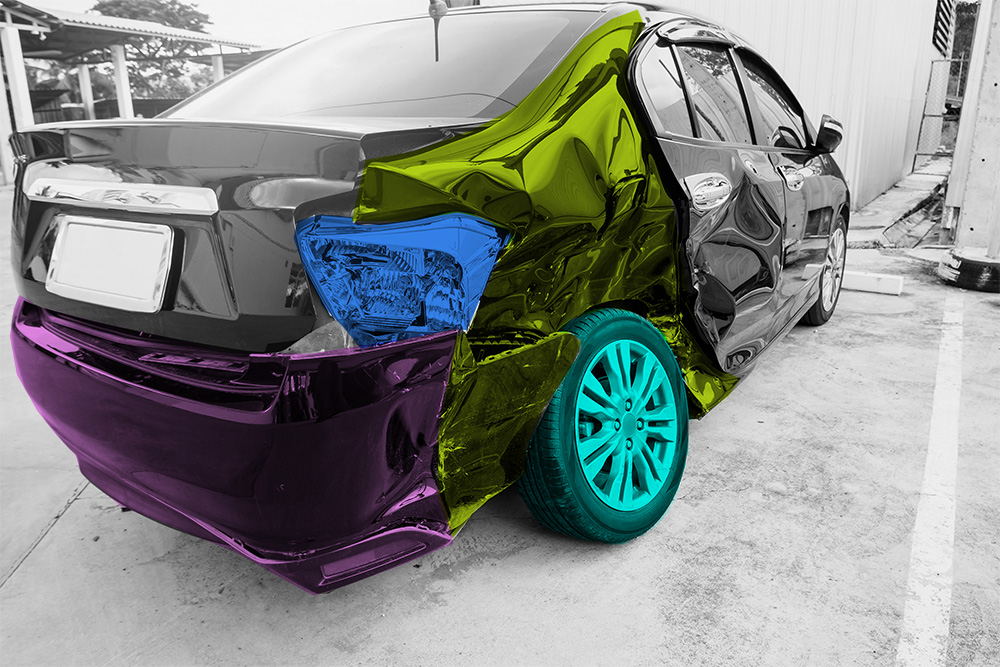
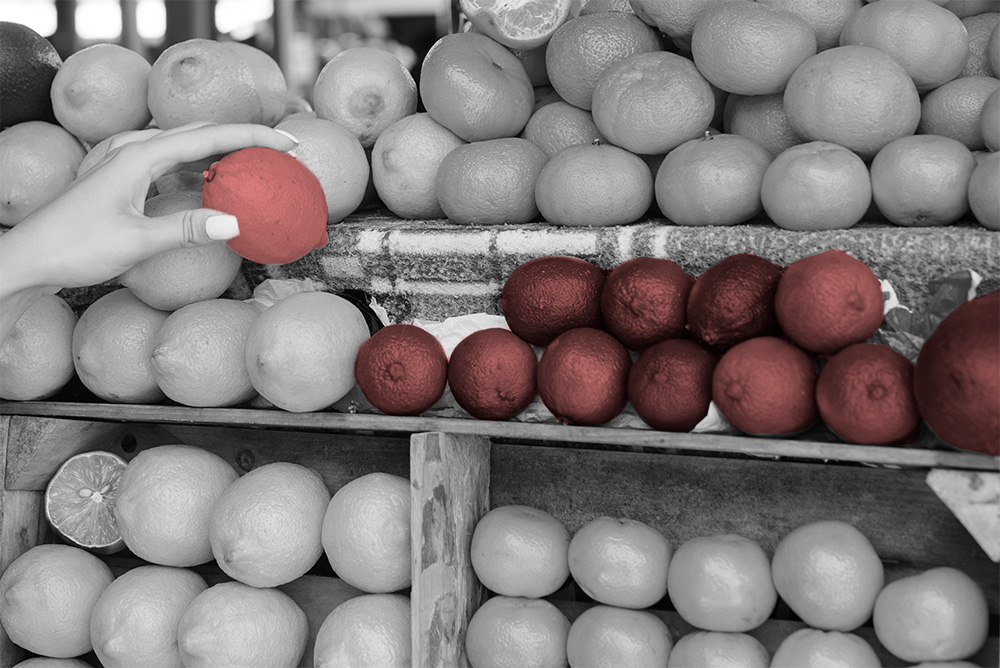
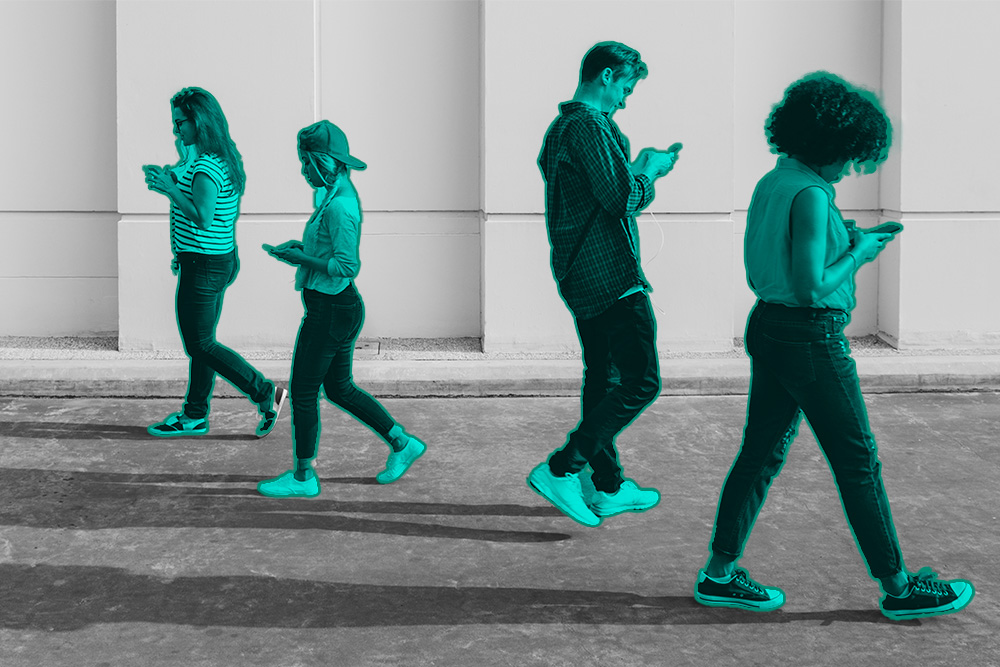
Imagine drawing a precise outline around an object in an image using a series of connected points. That’s the essence of polygon annotation. Unlike bounding boxes, which create rectangular enclosures around objects, often capturing unnecessary background areas, polygon annotation allows you to define the object’s exact boundaries with a closed polygonal shape.
Here’s a deeper dive into the key characteristics of polygon annotation:
- Unmatched Precision: Polygons provide a far more accurate representation of an object’s shape compared to bounding boxes. This is particularly advantageous for objects with intricate or irregular contours, such as a starfish or a bicycle. Bounding boxes would struggle to capture these shapes effectively, potentially leading to inaccurate data and hampering your machine learning model’s performance.
- Minimal Background Noise: By closely following an object’s outline, polygon annotations minimize the inclusion of irrelevant background data in your training dataset. This ensures your machine learning model focuses on the object of interest, not the clutter around it.
- Applications Across Industries: The versatility of polygon annotation makes it a valuable tool in various fields:
- Medical Imaging
- Medical Imaging
Precisely outlining organs, tumors, or other structures of interest is crucial for medical diagnosis and research. Polygon annotation allows for highly accurate segmentation of these intricate shapes.
- Autonomous Vehicles:

Self-driving cars rely on accurate perception of their surroundings. Polygon annotation helps segment lanes, traffic signs, pedestrians, and other vital elements for training models that navigate roads safely. - Object Detection and Recognition:

When training models to identify and classify objects in images, polygon annotation provides a clearer picture, leading to more accurate detection and recognition capabilities.
Why Choose Polygon Annotation Over Bounding Boxes?

Bounding boxes, while a simpler and faster annotation method, often introduce unwanted background data into your training set. This can lead to subpar performance in your machine learning models, especially when dealing with complex shapes. Here’s where polygon annotation shines:
- Enhanced Model Performance: The precise nature of polygon annotations translates to cleaner training data, ultimately resulting in better-performing machine learning models. With more accurate object representations, your models can learn to distinguish objects more effectively.
- Superior Object Segmentation: Polygon annotation is the go-to method for tasks like instance segmentation, where individual objects need to be differentiated from each other and the background. Bounding boxes often struggle in these scenarios, as they can group multiple objects into a single box.
- Reduced Labeling Errors: The ability to meticulously follow an object’s outline with polygons minimizes the chances of errors during the annotation process. This translates to a cleaner and more reliable training dataset for your machine learning models.
How is Polygon Annotation Done?
Polygon annotation can be efficiently performed using specialized software tools that provide features designed to streamline the process:
- Crystal-Clear Image Visualization: These tools ensure you have a clear view of the image while placing your polygon points, allowing for precise annotation.
- Effortless Polygon Creation: The software offers intuitive tools to create closed shapes by connecting points around the object’s boundary.
- Attribute Labeling: You can assign labels or categories to the objects being annotated, further enriching your training data.
Many companies offer annotation software solutions with robust polygon annotation capabilities. Choosing the right tool depends on your specific project requirements and budget.
The Compelling Benefits of Polygon Annotation
Integrating polygon annotation into your machine learning workflow unlocks a multitude of advantages:
- Unmatched Accuracy: By providing a more accurate representation of object boundaries, polygon annotation leads to better-trained models with improved accuracy in tasks like object detection and segmentation. This translates to real-world applications that perform more reliably.
- Reduced Annotation Time: While initially appearing more time-consuming than bounding boxes, polygon annotation can save time in the long run. The higher precision minimizes the need for re-annotation due to errors, leading to a more efficient workflow.
- Superior Data Quality: Cleaner training datasets with minimal background noise contribute significantly to the overall quality of your machine learning models. Polygon annotation ensures your models are trained on data that accurately reflects the real world, leading to superior performance.
Conclusion
Polygon annotation is the secret weapon for unlocking superior machine learning models. Its precise object labeling empowers you to achieve unmatched accuracy in tasks like object detection and segmentation. If your AI project demands results, don’t settle for anything less than expert-grade polygon annotation. Get a free quote today and see how our Polygon Annotation service can supercharge your AI development!