High Quality LiDAR Annotation: Advanced Insights for Precision AI
For professionals in the AI industry, high quality LiDAR annotation is the backbone of training cutting-edge algorithms.
At Subul Data Annotation, we go beyond basic annotation by applying deep domain expertise and advanced methodologies to unlock the full potential of 3D point cloud data. This article delves into the intricate processes and specialized techniques that set our services apart.
Advanced Techniques in LiDAR Annotation
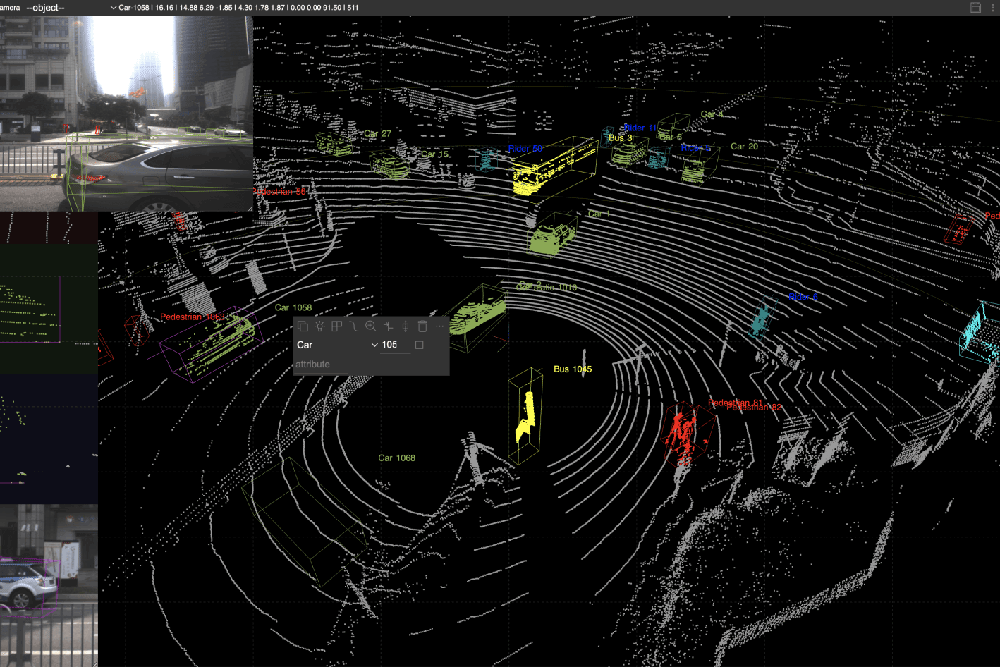
Dynamic Object Tracking
One of the most challenging aspects of LiDAR annotation is accurately labeling dynamic objects, such as moving vehicles or pedestrians. Our team uses:
- Frame-to-Frame Tracking: Ensuring continuity of object labels across multiple frames.
- Temporal Consistency Algorithms: Mitigating annotation drift in long sequences.
- Custom Labeling Protocols: Adapting guidelines for specific scenarios, such as high-speed environments or crowded urban areas.
Semantic and Instance Segmentation
LiDAR datasets often require both semantic segmentation (categorizing each point into classes like road, tree, or building) and instance segmentation (distinguishing individual objects within a class). Our workflow includes:
- Advanced Clustering Algorithms: Using DBSCAN, K-Means, and hierarchical clustering to isolate objects accurately.
- Class-Specific Annotation: Applying unique methodologies for complex objects like bicycles, construction equipment, and vegetation.
- Refinement Layers: Adding post-processing steps for maximum accuracy.
Multi-Sensor Fusion
Modern LiDAR annotation often involves combining data from multiple sensors, such as cameras and radars. Our team excels in:
- Sensor Calibration: Aligning data from multiple modalities for cohesive annotation.
- Cross-Sensor Validation: Using one sensor’s data to verify the annotations of another.
- Enhanced Depth Mapping: Leveraging fusion techniques to improve depth perception in challenging environments.
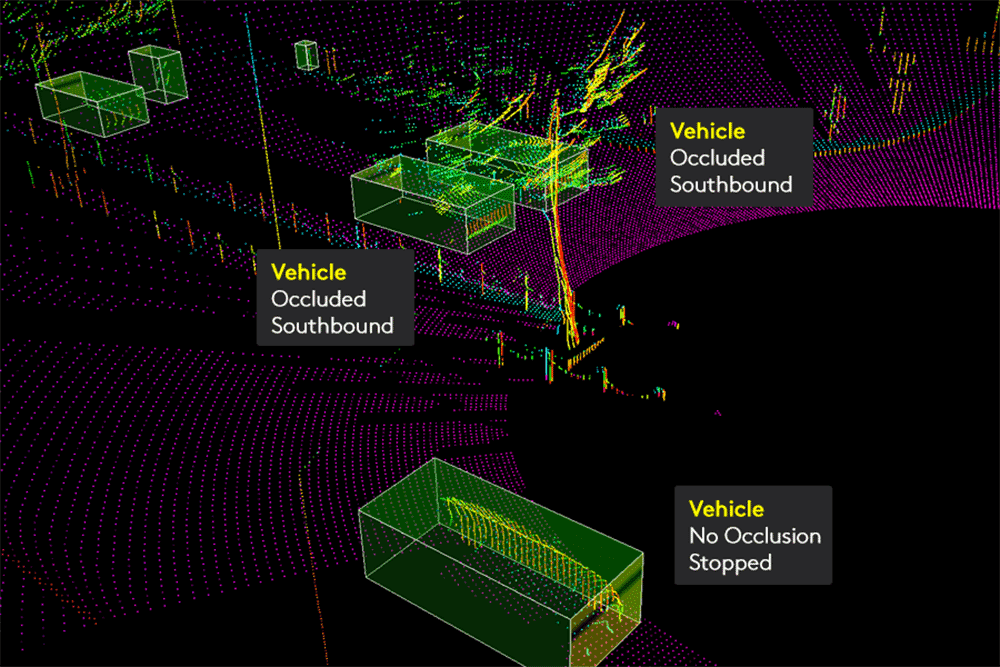
Edge Case Handling
AI systems often fail in rare or unusual scenarios. Our team identifies and annotates edge cases, such as:
- Obscured Objects: Labeling partially visible objects in dense environments.
- Weather Variations: Annotating datasets captured in rain, fog, or snow.
- Nighttime Data: Ensuring reliable annotations under low-light conditions.
Quality Assurance Processes
Achieving high quality LiDAR annotation requires rigorous quality assurance (QA). Our QA processes involve:
- Multi-Layer Review: Each annotation passes through multiple reviewers with domain expertise.
- Automated Validation Tools: Using in-house tools to detect inconsistencies and flag anomalies.
- Feedback Loops: Incorporating client feedback iteratively to refine the annotation process.
Innovations in Tooling and Workflow
At Subul, we continuously innovate to enhance efficiency and accuracy. Some of our proprietary tools and techniques include:
- Adaptive Annotation Platforms: Software that adjusts labeling interfaces based on data characteristics, improving annotator efficiency.
- Hybrid Approaches: Combining manual annotation with AI-assisted tools to balance accuracy and speed.
- Custom Export Pipelines: Delivering annotations in formats optimized for client-specific machine learning frameworks.
Emerging Applications of LiDAR Annotation
Environmental Monitoring
LiDAR annotation is revolutionizing how we monitor and analyze environmental data:
- Forest Mapping: Identifying tree species, density, and health.
- Coastal Erosion Tracking: Annotating shoreline changes for mitigation planning.
- Wildlife Monitoring: Detecting and tracking animal movements in natural habitats.
Smart Cities
For smart city initiatives, LiDAR data is crucial for:
- Traffic Flow Analysis: Annotating vehicle and pedestrian patterns to optimize urban planning.
- Infrastructure Maintenance: Monitoring road and bridge conditions through annotated datasets.
- Public Safety: Enhancing surveillance systems with precise object detection.
Agriculture Technology
LiDAR annotation supports precision agriculture by:
- Crop Health Analysis: Identifying variations in plant health through 3D mapping.
- Yield Prediction: Annotating datasets for predictive modeling of crop output.
- Equipment Navigation: Guiding autonomous farming equipment with annotated terrain data.
Industry-Specific Expertise
Autonomous Driving
For self-driving systems, we provide:
- High-Resolution 3D Mapping: Annotating LiDAR data for HD maps.
- Obstacle Detection: Labeling objects like barriers and construction zones.
- Behavior Prediction: Annotating trajectories of moving objects for predictive modeling.
Robotics and Warehousing
In robotics, LiDAR annotation enables:
- Object Grasping: Precise labeling of items for robotic arms.
- Path Planning: Annotating environmental features to guide autonomous navigation.
- Inventory Management: Labeling objects in 3D point clouds for efficient stock tracking.
Infrastructure and Utilities
For infrastructure projects, we focus on:
- Power Line Detection: Annotating utility lines and poles in aerial LiDAR datasets.
- Terrain Analysis: Segmenting ground and non-ground points for land-use planning.
- Pipeline Inspection: Identifying potential issues in underground and overhead pipelines.
Overcoming Common LiDAR Annotation Pitfalls
- Ambiguous Boundaries: Implementing advanced edge-detection techniques to resolve unclear object boundaries.
- Data Artifacts: Cleaning and preprocessing raw data to remove noise and distortions.
- Scale Variations: Using multi-scale approaches to annotate both macro and micro-level features.
- Annotation Fatigue: Implementing annotator rotation schedules to maintain high performance over extended projects.
Research and Development in LiDAR Annotation
To stay ahead of the curve, Subul invests in ongoing R&D to:
- Develop New Algorithms: Enhancing annotation speed and accuracy through machine learning.
- Optimize Workflows: Streamlining processes for large-scale datasets.
- Collaborate with Academia: Partnering with universities to refine annotation standards and explore new applications.